AFB rapid culture by MGIT - Sputum
New
2000₹
In stock
Hyderabad
0 Reviews
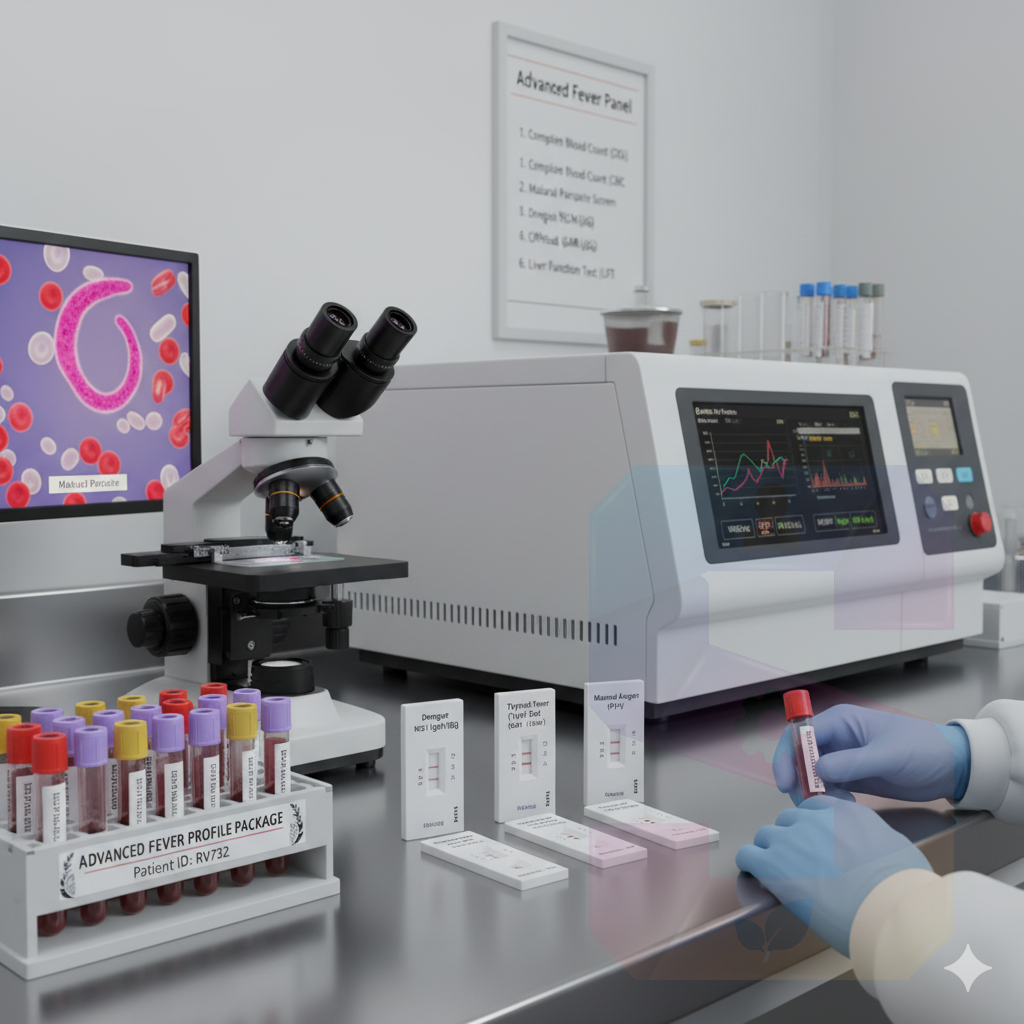
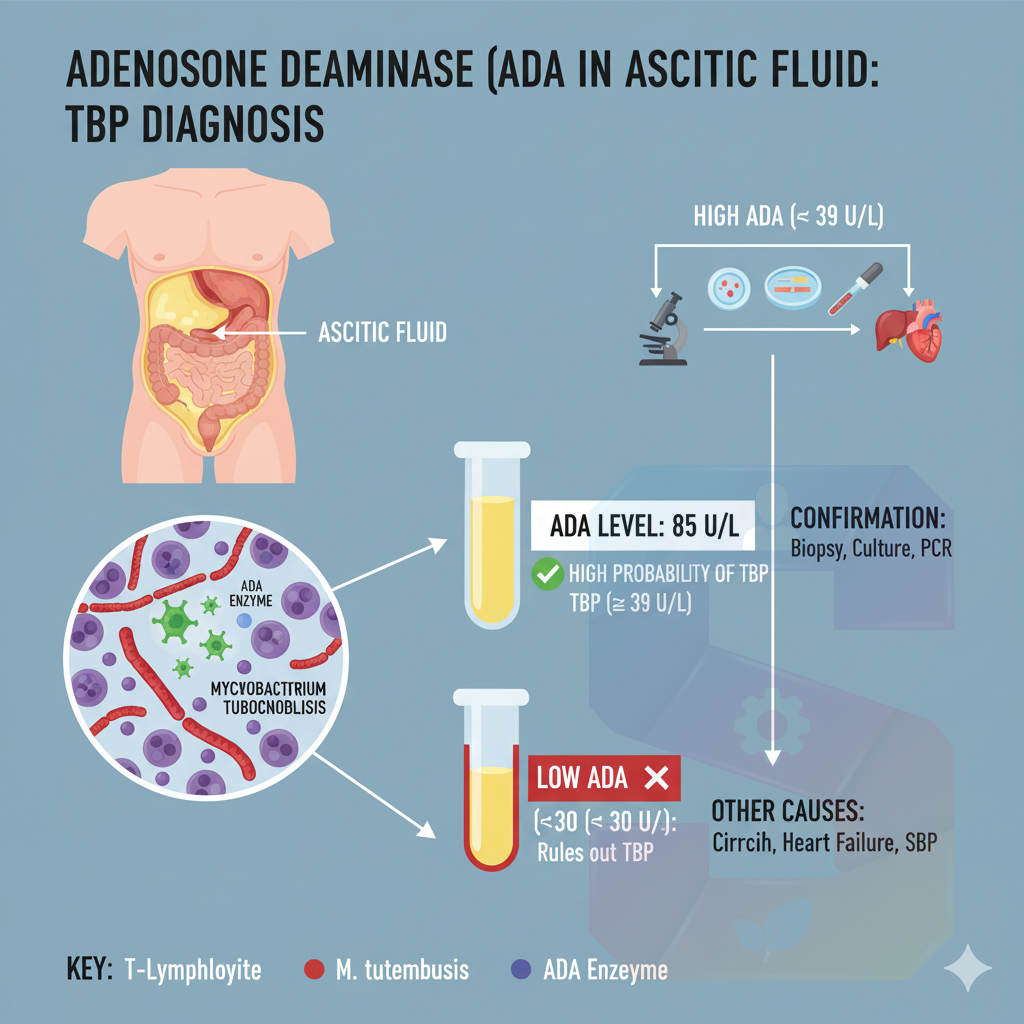
The Mycobacteria Growth Indicator Tube (MGIT) system is the primary automated liquid culture method used globally for the rapid and sensitive detection of Acid-Fast Bacilli (AFB), predominantly Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB Complex), in sputum and other respiratory samples.
Rapid Time to Detection (TTD): This is the key benefit. MGIT reduces the culture positivity time compared to traditional solid media (like Lowenstein-Jensen, LJ).
MGIT TTD: Typically 10–14 days for positive cases (often reported negative after 42 days).
Solid Media TTD: Can take 3–8 weeks.
Increased Sensitivity: The liquid medium is superior for mycobacterial recovery, particularly for smear-negative sputum samples where the bacterial load is low. This enhances the diagnosis of less infectious cases.
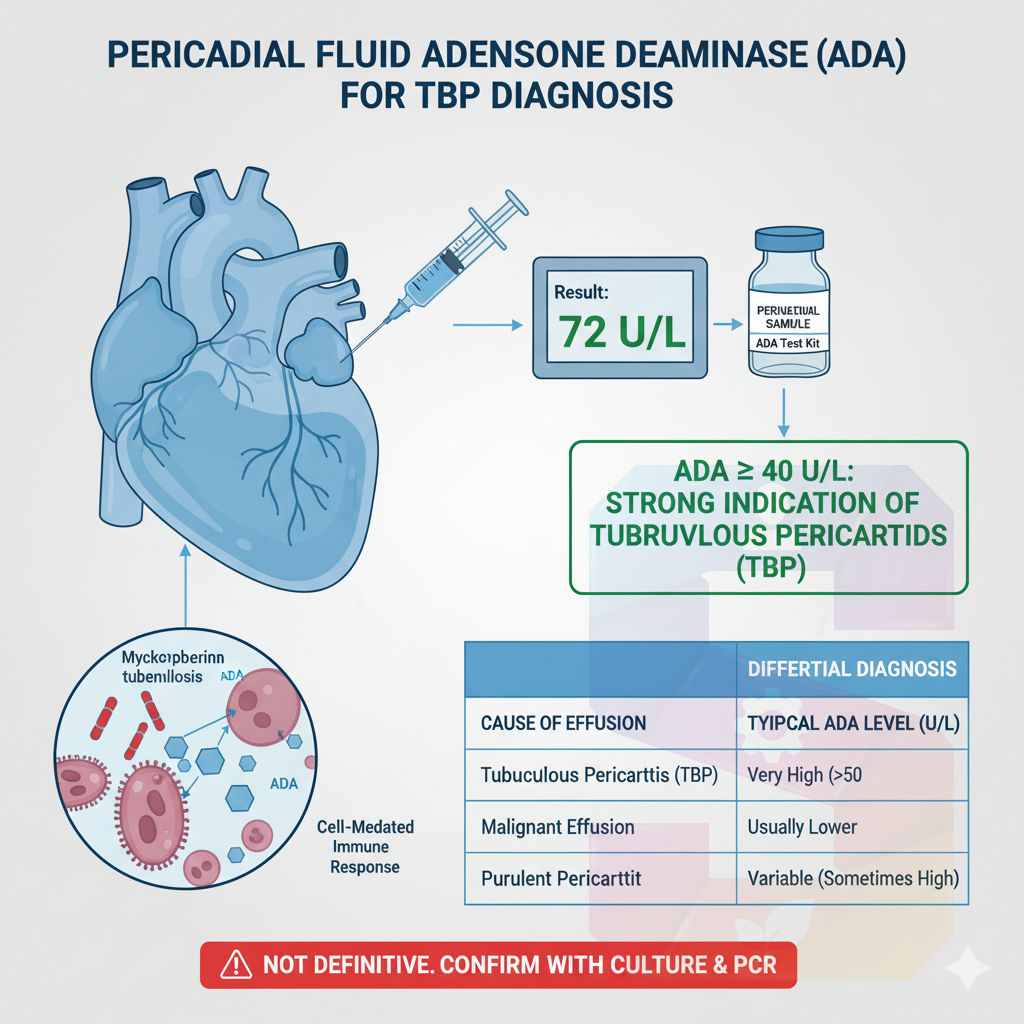
Definitive Diagnosis: Provides the "gold standard" confirmation of active pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) or Non-tuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM) infection.
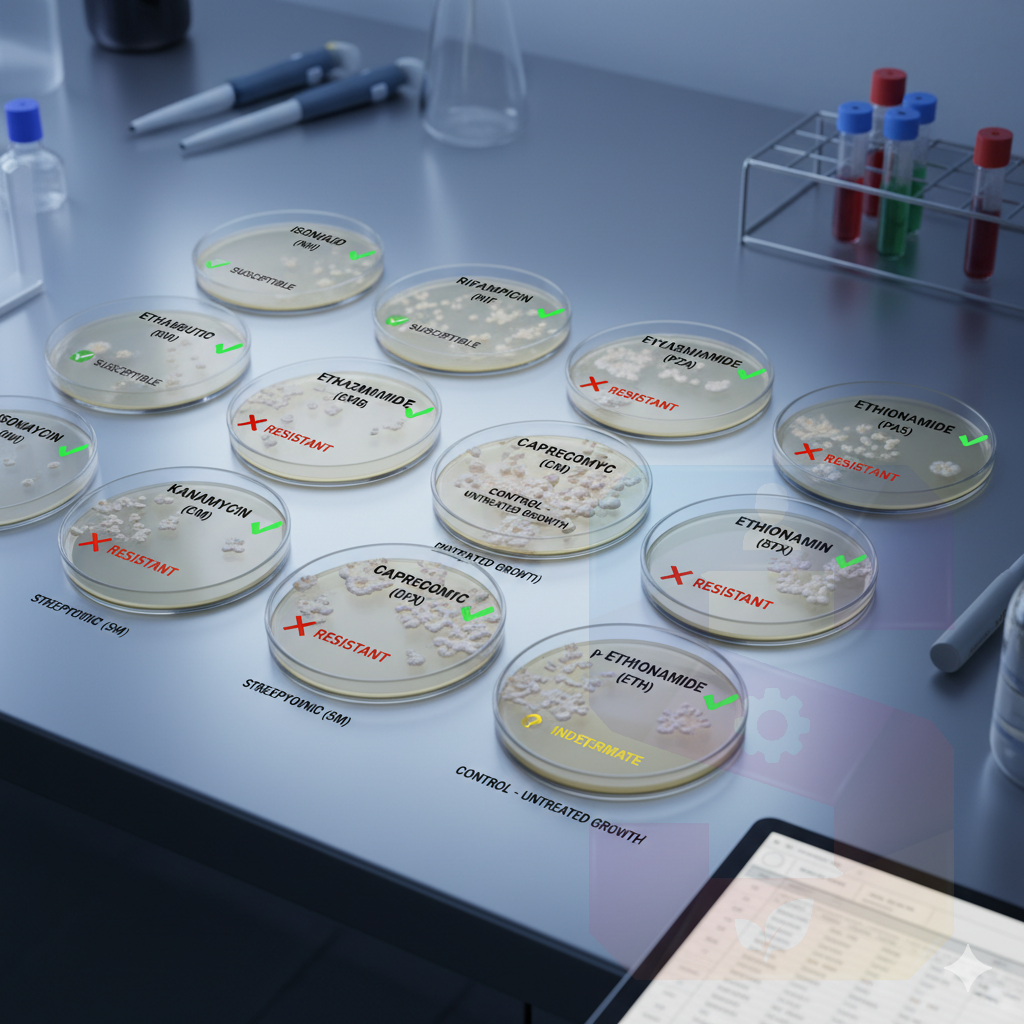
Downstream Testing: A positive MGIT culture provides a liquid inoculum that is ideal for rapid Drug Susceptibility Testing (DST), which is crucial for identifying Multi-Drug Resistant TB (MDR-TB).
Monitoring Treatment: Can be used to monitor the efficacy of anti-TB treatment by observing the Time to Detection (TTD) of follow-up sputum samples.
Rapid Time to Detection (TTD): This is the key benefit. MGIT reduces the culture positivity time compared to traditional solid media (like Lowenstein-Jensen, LJ).
MGIT TTD: Typically 10–14 days for positive cases (often reported negative after 42 days).
Solid Media TTD: Can take 3–8 weeks.
Increased Sensitivity: The liquid medium is superior for mycobacterial recovery, particularly for smear-negative sputum samples where the bacterial load is low. This enhances the diagnosis of less infectious cases.
Definitive Diagnosis: Provides the "gold standard" confirmation of active pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) or Non-tuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM) infection.
Downstream Testing: A positive MGIT culture provides a liquid inoculum that is ideal for rapid Drug Susceptibility Testing (DST), which is crucial for identifying Multi-Drug Resistant TB (MDR-TB).
Monitoring Treatment: Can be used to monitor the efficacy of anti-TB treatment by observing the Time to Detection (TTD) of follow-up sputum samples.
The Mycobacteria Growth Indicator Tube (MGIT) system is the primary automated liquid culture method used globally for the rapid and sensitive detection of Acid-Fast Bacilli (AFB), predominantly Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB Complex), in sputum and other respiratory samples.
Rapid Time to Detection (TTD): This is the key benefit. MGIT reduces the culture positivity time compared to traditional solid media (like Lowenstein-Jensen, LJ).
MGIT TTD: Typically 10–14 days for positive cases (often reported negative after 42 days).
Solid Media TTD: Can take 3–8 weeks.
Increased Sensitivity: The liquid medium is superior for mycobacterial recovery, particularly for smear-negative sputum samples where the bacterial load is low. This enhances the diagnosis of less infectious cases.
Definitive Diagnosis: Provides the "gold standard" confirmation of active pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) or Non-tuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM) infection.
Downstream Testing: A positive MGIT culture provides a liquid inoculum that is ideal for rapid Drug Susceptibility Testing (DST), which is crucial for identifying Multi-Drug Resistant TB (MDR-TB).
Monitoring Treatment: Can be used to monitor the efficacy of anti-TB treatment by observing the Time to Detection (TTD) of follow-up sputum samples.
0 Comments
0 Shares
226 Views
0 Reviews